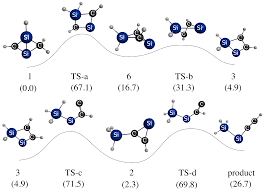
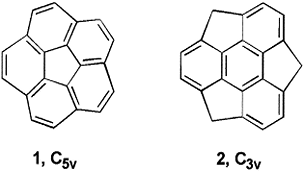
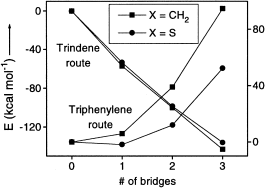
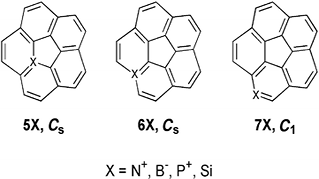
Hybrid density functional theory (DFT) calculations at the B3LYP/cc-pVDZ level have been performed on a series of heterobuckybowls, 3X, C18X3H6 (X = O, NH, CH2, BH, S, PH, PH3, Si, SiH2, and AlH). The minimum energy conformations and the transition states for bowl-to-bowl inversion, where the geometry is bowl shaped, are computed and characterized by frequency calculations. The geometries of heterotrindenes, 2X, C12X3H6 (X = O, NH, CH2, BH, S, PH, PH3, Si, SiH2, and AlH), were obtained, and the bond length alternation (Δ) in the central benzenoid ring shows remarkable sensitivity as a function of substituent with a wide range of fluctuations (−0.014 to +0.092 Å). The Δ computed in 2BH was found to be comparable with the highest bond alternation reported to date in benzenoid frameworks. The inversion dynamics of these heterobowls and their bowl depths were fit to a mixed quartic/quadratic function. The size of the heteroatom seems to exclusively control the bowl depth and rigidity as well as the synthetic feasibility. In contrast, the bond length alternation seems to be controlled by electronic factors and not by the size of the substituted atom either in trindenes or in heterosumanenes. The thermodynamic stability of this class of compounds is very much comparable with trithiasumanene (3S), which has been synthesized recently. The chemical hardness (η) was measured to assess the stability of the heterosumanenes. The strain energy buildup in a sequential ring closure strategy along two synthetic routes, namely a triphenylene route and a trindene route, were explored, and the trindene route was found to be highly favorable for making such compounds compared to the triphenylene route. However, in both routes the ease of the synthetic feasibility increases as the size of the heteroatom increases.