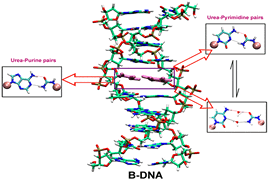
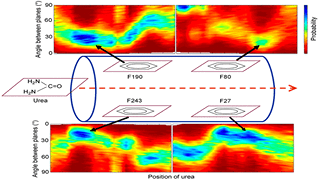
Urea lesions are formed in DNA because of free radical damage of the thymine base, and their occurrence in DNA blocks DNA polymerases, which has deleterious consequences. Recently, it has been shown that urea is capable of forming hydrogen bonding and stacking interactions with nucleobases, which are responsible for the unfolding of RNA in aqueous urea. Base pairing and stacking are inherent properties of nucleobases; because urea is able to form both, this study attempts to investigate if urea can mimic nucleobases in the context of nucleic acid structures by examining the effect of introducing urea lesions complementary to the four different nucleobases on the overall helical integrity of B-DNA duplexes and their thermodynamic stabilities using molecular dynamics (MD) simulations. The MD simulations resulted in stable duplexes without significant changes in the global B-DNA conformation.

G Suresh, S Padhi, I Patil, UD Priyakumar