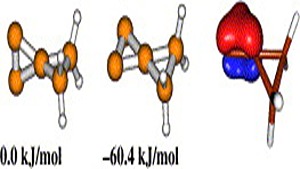
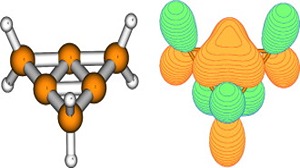
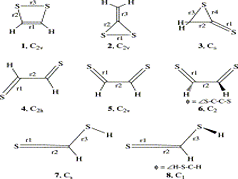
Ab initio (MP2, CCSD(T)) and hybrid density functional theory (B3LYP) calculations with up to triple-ζ basis set were done to locate all possible minima, where each carbon in the molecule is tetracoordinate, on the C6H6 potential energy surface. The search was initiated with a total of 218 structures, and in few cases, geometrical and stereoisomers were considered. The exhaustive study on all these topological structures resulted in a total of 263 stationary points on the C6H6 potential energy surface. The B3LYP level characterizes 209 as minima, 31 as transition states, 8 as second-order, 7 as third-order, and 1 as fourth-order saddle points. The remaining 7 structures could be located as stationary points only at the MP2 level. The molecules were classified into acyclic, monocyclic, bicyclic, tricyclic, and tetracyclic. The acyclic isomers fall within a range of 60−80 kcal/mol higher in energy compared to benzene. Among the cyclic structures, the range of relative stabilities of minima is larger, viz., monocyclic (31−146 kcal/mol), bicyclic (72−159 kcal/mol), tricyclic (72−300 kcal/mol), and tetracyclic (102−156 kcal/mol). Strain due to small three and four membered rings and constrained double and triple bonds control the relative stabilities of these isomers. The computed isomers exhibit various novel bonding modes for carbon, namely, planar tetracoordinate, hypervalent, pyramidal, bent/twisted double bonds, vicinal dicarbenes, nonlinear triple bonds, and so forth. Absolute chemical hardness values have no correlation with the relative stabilities, and about 45 molecules have higher hardness values than that of benzene.