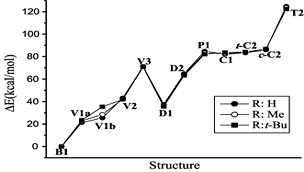
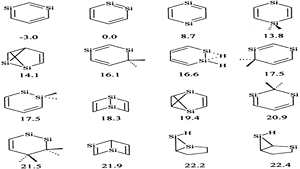
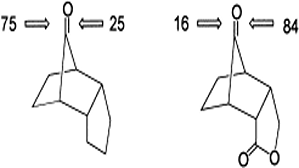
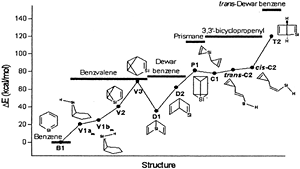
Density functional theory (B3LYP) calculations were performed on the methyl and t-butyl substituted valence isomeric forms of silabenzene. The recently identified 12 valence isomeric minima on the potential energy surface of silabenzene were considered. The calculations reveal that substitution does not affect the skeleton of all the compounds including the unusual structures, V1a and V1b, located on the silabenzene potential energy surface. Similarly, the geometric parameters and relative energies show negligible differences upon substitutions by Me and t-Bu groups except for V1b. Chemical hardness and frontier orbital energy levels are used to assess the reactivity change upon substitution. The present study concludes that the substitution by Me or t-Bu will have only the steric effect and therefore, theoretical models employing the unsubstituted analogues should adequately describe the structural and energetic characteristics of the bulky group substituted silaaromatic compounds.

DM Dhevi, UD Priyakumar, GN Sastry,