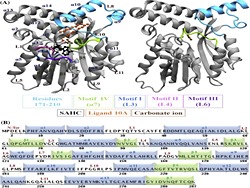
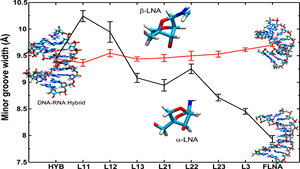
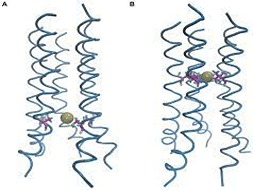
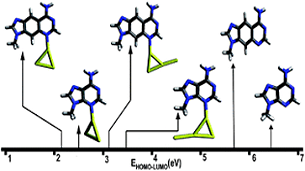
Mycobacterial cyclopropane synthase 1 (CmaA1) is one of the most important drug targets in anti tuberculosis drug discovery as it is responsible for cis-cyclopropanation at the distal position of unsaturated mycolates, which is an essential step for the pathogenicity, persistence and drug resistance.

C Choudhury, UD Priyakumar, GN Sastry