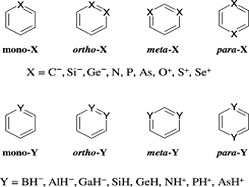
Ab initio HF, MP2, CCSD(T) and hybrid density functional B3LYP calculations were performed on a series of skeletally mono- and di-substituted benzenes, (CH)5Z and (CH)4Z2, Z = C–, N, O+, Si–, P, S+, Ge–, As, Se+, BH–, NH+, AlH–, SiH, PH+, GaH–, GeH and AsH+. Various measures of aromaticity such as the bond length equalization, homodesmic equations, singlet-triplet energy difference (AE s-t), chemical hardness (η) and out-of-plane distortive tendency are critically analysed. The relative energy ordering in skeletally disubstituted benzenes displays trends that are inexplicable based on conventional wisdom. In general, the orthoisomer is found to be the least stable when the substituent is from the second row, whereas if the substituent is from the fourth row, the ortho-isomer is the most stable. Various qualitative arguments, including (a) lone pair-lone pair repulsion, (b) the sum of bond strengths in the twin Kekule forms, and (c) the rule of topological charge stabilization (TCS), are used to explain the observed relative energy trends. The rule of TCS in conjunction with the sum of bond strengths is found to predict the relative energy ordering reasonably well. The reactivity of this class of compounds is assessed based on their singlet-triplet energy differences, chemical hardness and the frequencies corresponding to out-of-plane skeletal distortions. These reactivity indices show less kinetic stability for the compounds with substituents from the fourth row and point to the fact that the thermodynamically most stable compounds need not be the least reactive ones. The ‡Es-t values indicate that the π-framework of benzene weakens upon skeletal substitutions.