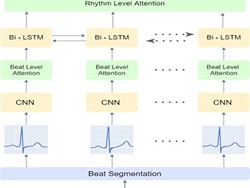
Early detection of cardiovascular diseases is crucial for effective treatment and an electrocardiogram (ECG) is pivotal for diagnosis. The accuracy of Deep Learning based methods for ECG signal classification has progressed in recent years to reach cardiologist-level performance. In clinical settings, a cardiologist makes a diagnosis based on the standard 12-channel ECG recording. Automatic analysis of ECG recordings from a multiple-channel perspective has not been given enough attention, so it is essential to analyze an ECG recording from a multiple-channel perspective.

U. Deva Priyakumar,Likith Reddy; Vivek Talwar; Shanmukh Alle; Raju. S. Bapi