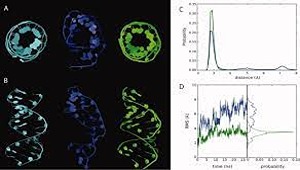
Here, we present an update of the CHARMM27 all-atom additive force field for nucleic acids that improves the treatment of RNA molecules. The original CHARMM27 force field parameters exhibit enhanced Watson-Crick base pair opening which is not consistent with experiment, whereas analysis of molecular dynamics (MD) simulations show the 2′-hydroxyl moiety to almost exclusively sample the O3′ orientation. Quantum mechanical (QM) studies of RNA related model compounds indicate the energy minimum associated with the O3′ orientation to be too favorable, consistent with the MD results. Optimization of the dihedral parameters dictating the energy of the 2′-hydroxyl proton targeting the QM data yielded several parameter sets, which sample both the base and O3′ orientations of the 2′-hydroxyl to varying degrees. Selection of the final dihedral parameters was based on reproduction of hydration behavior as related to a survey of crystallographic data and better agreement with experimental NMR J-coupling values. Application of the model, designated CHARMM36, to a collection of canonical and noncanonical RNA molecules reveals overall improved agreement with a range of experimental observables as compared to CHARMM27. The results also indicate the sensitivity of the conformational heterogeneity of RNA to the orientation of the 2′-hydroxyl moiety and support a model whereby the 2′-hydroxyl can enhance the probability of conformational transitions in RNA.