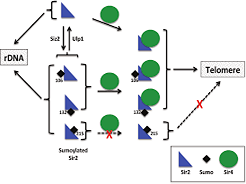
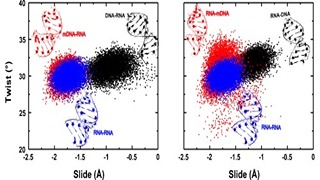
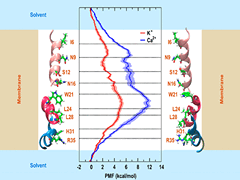
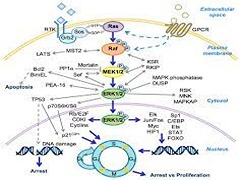
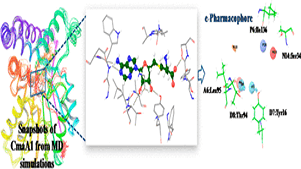
Silent information regulator 2 (Sir2), the founding member of the conserved sirtuin family of NAD(+)-dependent histone deacetylase, regulates several physiological processes including genome stability, gene silencing, metabolism and life span in yeast. Within the nucleus, Sir2 is associated with telomere clusters in the nuclear periphery and rDNA in the nucleolus and regulates gene silencing at these genomic sites. How distribution of Sir2 between telomere and rDNA is regulated is not known.

A Hannan, NM Abraham, S Goyal,I Jamir, UD Priyakumar, K Mishra